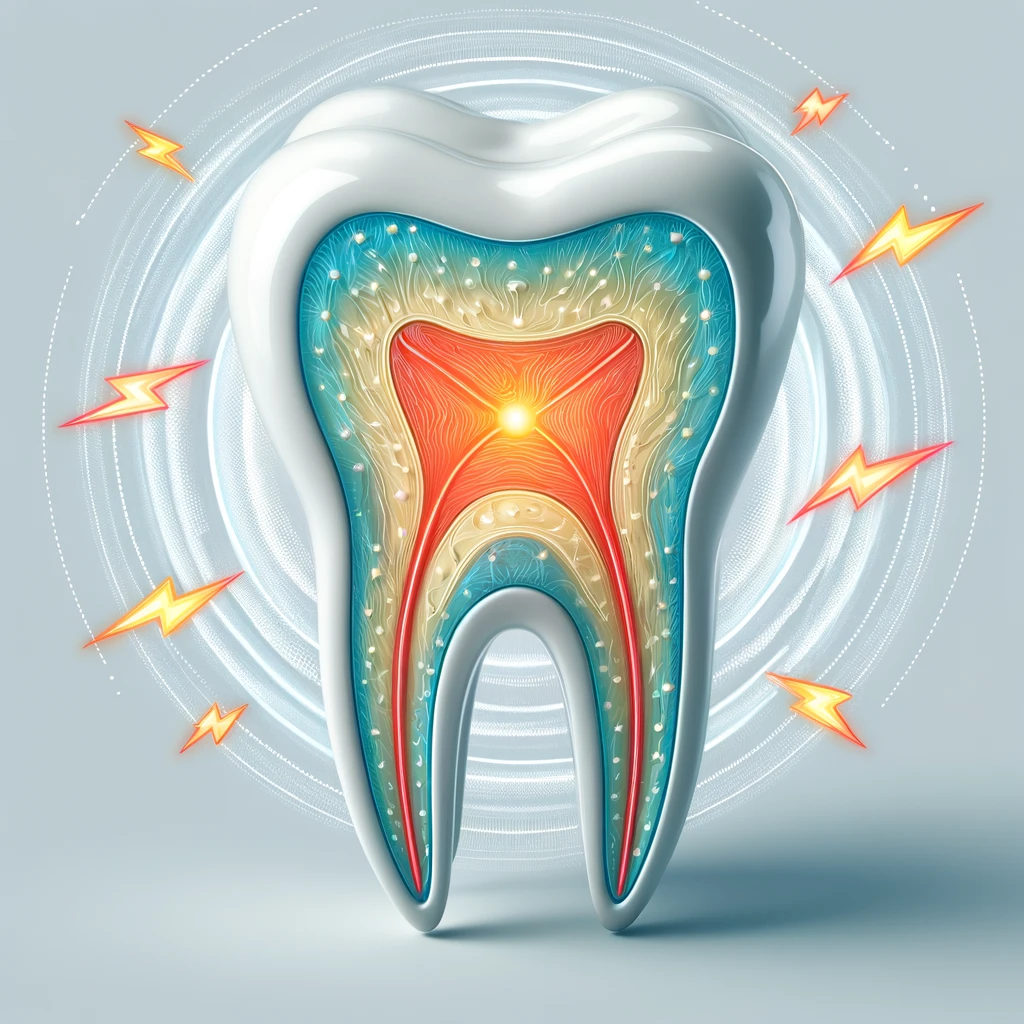
Tooth sensitivity is a condition marked by discomfort or sharp pain. It triggers by hot, cold, sweet, acidic foods or even cold air.
Nature has made our teeth in three layers, Enamel, Dentin and Cementum. The enamel is the outermost layer which is hardest substance in the human body. It is a protective shield for our teeth.It acts as a barrier against the wear and tear caused by regular chewing and biting. We unknowingly damage the enamel in various ways which uncover the Dentin. It contains tiny tubules leading to the tooth nerve which causes tooth sensitivity. Maintaining healthy enamel, therefore, is highly essential for preventing tooth sensitivity.
How does enamel damage?
Overconsumption of acidic foods and drinks (such as citrus and soda) can erode the enamel, exposing the dentin underneath. Tooth decay leads to cavities, which create pathways for stimuli to reach the dentin. Grinding or clenching teeth can wear down the enamel, resulting in sensitivity. Using a hard-bristled toothbrush or brushing too aggressively can cause enamel abrasion. Frequent vomiting or stomach acid reflux associated with eating disorders can also erode the enamel over time.
Tooth whitening can sometimes lead to tooth sensitivity. This is due to the bleaching agents used in the process, which penetrates the enamel and reach the dentin, exposing the nerves within the tooth. It causes increased tooth sensitivity to hot, cold, sweet, and acidic substances.
Tooth sensitivity due to gum recession occurs when the gum tissue pulls away from the tooth, exposing the root surface. The root is not protected by enamel, leaving it vulnerable to hot, cold, sweet, and acidic stimuli. This can lead to tooth sensitivity. Gum recession often results from gum disease or aggressive brushing techniques.
Tooth Sensitivity following a recent dental procedure is a common occurrence. It can arise from various treatments like fillings, crowns, or root canals. During these procedures, the tooth structure is altered, exposing sensitive dentin. Additionally, this sensitivity is usually temporary and subsides within a few days or weeks
Treatments for Tooth Sensitivity
Desensitizing Toothpaste: It contains ingredients that block pain signals from the tooth to the dentin reducing tooth sensitivity.
Proper Oral Hygiene: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush, non-abrasive toothpaste, and practice gentle brushing to prevent enamel erosion.
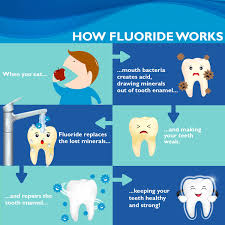
Fluoride Application: Professional application of fluoride varnish or gel strengthens enamel and reduces sensitivity in teeth.
Dental Bonding or Sealants: For exposed dentin or root surfaces, a dentist may apply bonding agents or sealants to protect the sensitive areas.
Night Guards: Custom-made guards can prevent enamel damage caused by teeth grinding during sleep.
Dental Restorations: Teeth sensitivity due to decay, cracks, or loose fillings may require restoration.
Treating Underlying Medical Conditions: Address conditions like acid reflux or eating disorders to prevent further enamel damage. It significantly reduces sensitivity in teeth.