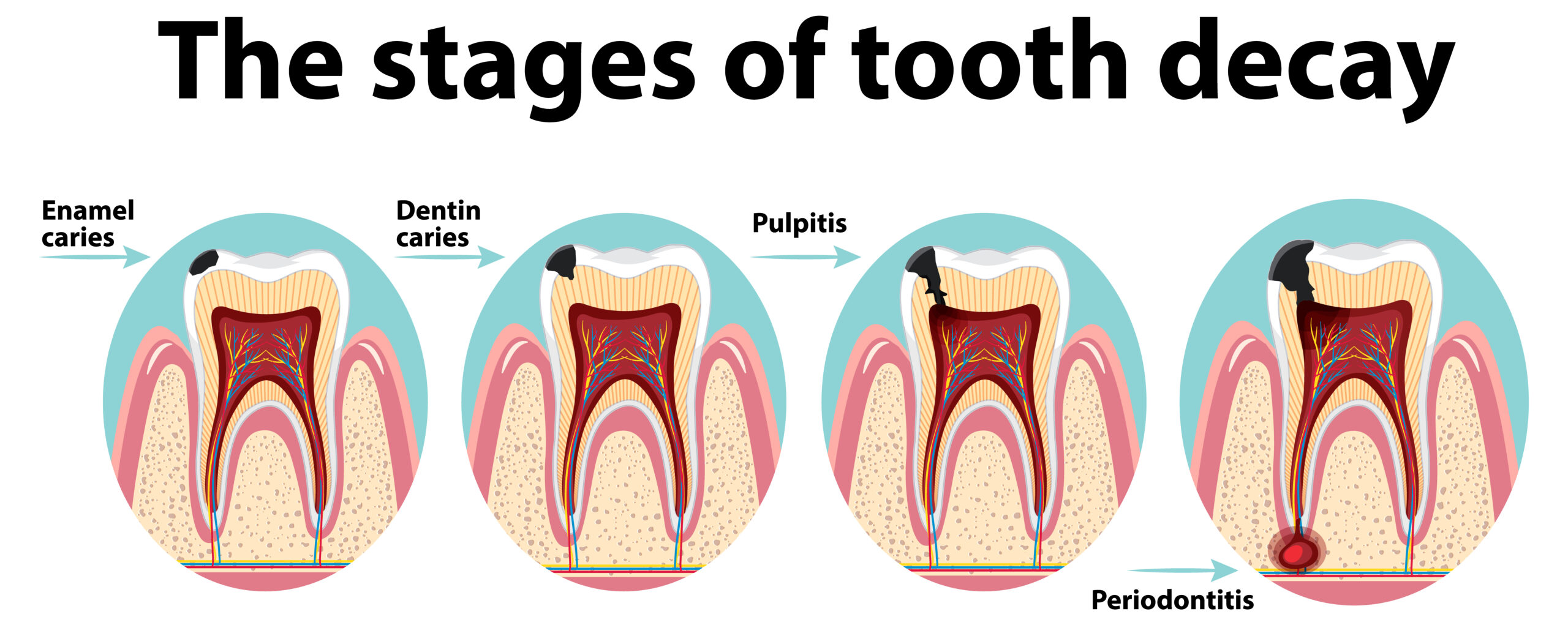
If the cavity reaches the deeper part of a tooth called the pulp, it can cause continuous or severe toothache. Dentists call it as a “deep tooth cavity. Patients feel pain especially when chewing or when the tooth is exposed to hot or cold stimuli. Pain may also occur spontaneously without any stimulus.
Your dentist may recommend “Pulp capping”. It is a dental procedure which preserves the vitality of the dental pulp where a deep cavity threatens to expose or has minimally exposed the pulp. It is a conservative treatment that prevents the need for root canal therapy or tooth extraction by promoting the healing and repair of the pulp tissue.
If a deep tooth cavity remains untreated, it leads to an infection in the pulp. It results in gum swelling, tenderness, and even the formation of a pus-filled abscess. If the decay (cavity) has reached the pulp, a root canal treatment (RCT) is necessary.
The root canal procedure involves removing the infected pulp, cleaning the root canals, and filling them with a special material. A crown is often placed over the tooth afterward to protect it.In severe cases where the tooth is extensively damaged or unsalvageable, extraction may be the only option. However, former option is preferred as RCT saves the natural tooth, preserving its structure and function which is essential for maintaining proper bite alignment, chewing ability, and speech.